by
Elizabeth Moran | Mar 20, 2013
Understanding what you invest in and how those investments perform in different markets is important. The recent increase in government bond yields and corresponding decline in prices is a case in point. Most investors would claim they don’t own any Commonwealth government bonds or state or territory bonds (known as semi-government bonds) yet managed funds and exchange traded funds (ETFs) specialising in bonds can hold large quantities.
Last year Commonwealth government bonds and semi-government bonds outperformed. Many of the bonds increased in price and sit well over par value of $100. For example the Commonwealth government May 2021 5.75% fixed rate bond (most government bonds are fixed rate although they do issue inflation linked bonds) is trading around $116.50 with a yield to maturity of 3.41% and a running yield of 4.94%. New South Wales Treasury Corporation have an April 2016 6.00% fixed rate bond that is trading at about $108 with a yield to maturity of 3.21% and a running yield of 5.56%. However, what we’re now witnessing is a rise in government bond yields in a “risk-on” market (not taking into account the failure of the Cypriot state over the weekend). That means investors have been selling low risk Commonwealth and semi-government bonds in preference for higher risk investments that pay higher returns. Commonwealth and semi-government bond prices have been declining.
This begs the question is it time to reconsider passive investment in fixed income via managed funds, particularly those with high allocations to government bonds? If clients can’t own direct fixed income, are managed funds still better than cash or listed hybrids?
Over the last five years managed bond funds have had high returns. They are reasonable fixed income investments if you can’t afford to build your own direct investment portfolio.
To gain an appreciation of whether a fund’s prices might move lower we need to assess four main factors:
- Is the fund actively or passively managed?
- The underlying benchmark on which the performance of the fund is being judged
- The percentage allocation to government bonds
- Expectations regarding government bond yields
1. Is the fund actively or passively managed?
An active fund manager will be buying and selling investments in the fund in an attempt to maximise return. It will be in their interest to crystallise government bond gains and to minimise the downside risk of the bond prices declining further.
In contrast a passive fund won’t have the oversight of an active manager. If their aim is to replicate the broader market, their fund will hold similar proportions of bonds as the underlying index. I’d suggest these managed funds are more at risk of loss from a decline in government bond prices.
2. The underlying benchmark on which the performance of the fund is being judged
The most commonly used benchmark is the UBS Bond Composite Index. This index has a high weighting to Commonwealth and semi-government bonds of 67.3%. The other sectors in the Index are supra-nationals (defined by Investopedia as An international organisation, or union, whereby member states transcend national boundaries) with 18.3% and corporate bonds 14.4%.
A passively managed fund should hold an allocation close to the benchmark it is trying to replicate which would mean most passive funds have a high exposure to Commonwealth government and semi-government bonds.
3. The percentage allocation to government bonds and fund performance
In Table 1 below we show four Australian managed bond funds. The allocation to government bonds varies between 17.0% for the Pimco Wholesale Australian Focus Fund to 56.6% for the Russell Australian Bond Fund (although the latest available portfolio allocation dates differ for the funds). The table also includes two exchange traded funds (ETFs) with almost 100% weightings to government bonds.
All the managed funds state they are actively managed, yet the returns and fees differ significantly. Interestingly, the PIMCO Wholesale Australian Focus Fund underperformed and has the lowest allocation to government bonds with a net one year return of 7.39% to 28 February 2013. All three of the other funds have a higher allocation to government bonds and higher returns.
Without knowing exactly what the funds hold and all the trades made during the year, it’s difficult to ascertain the reason for the higher returns.
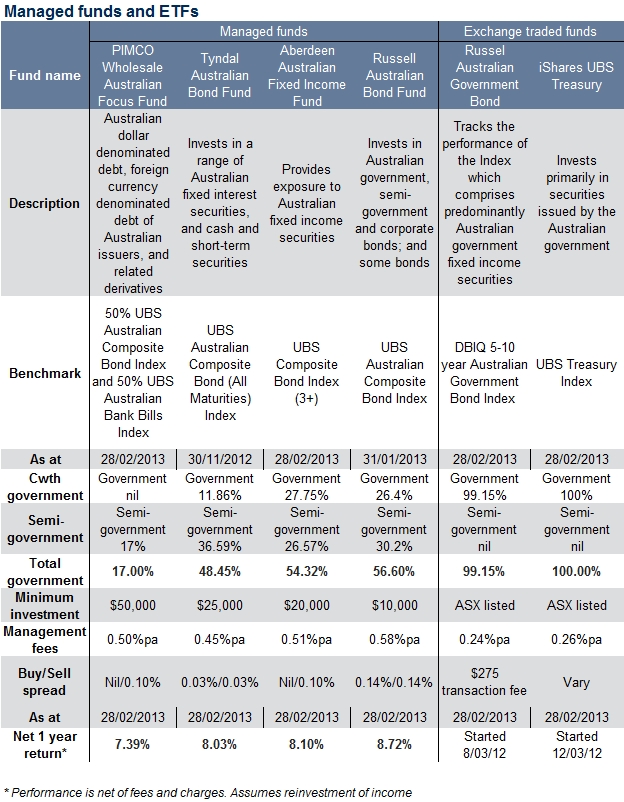
Source: Company websites
Table 1
1. Expectations regarding government bond yields
If you expected that we were in for a period of growth and increasing interest rates in an attempt to limit growth, then you would be a seller of fixed rate government bonds (including managed funds with a high allocation to government bonds) as you would have the expectation that yields would increase and fixed rate bond prices would decline.
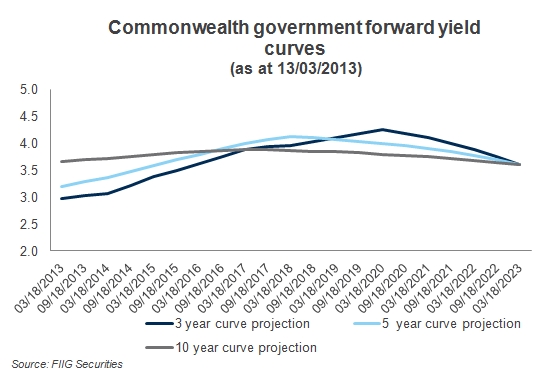
One way bond analysts measure expectations is by assessing the markets’ expectations of forward interest rates. Figure 1 below shows the market’s expectation of the future rates for three, five and ten year government bonds, the lines on the graph are known as the Commonwealth government yield curves.
Little upward movement is shown, so the market doesn’t expect any large increases in yield, although the market has been wrong in the past.
Commentary
While investors are happy buying higher risk assets the Cypriot default over the weekend highlights the fragile state of the global economy. Foreign investors still view our government bonds as good relative value, although prices of the bonds have been declining.
Direct bond investment can result in outperformance compared to other fixed income investments (see “The top bond picks”). I continue to think direct investment is best. It allows investors to own bonds in companies they chose and to buy and sell when it suits them. But, with the minimum investment of $50,000 for FIIG’s DirectBonds, this market isn’t available to all investors. I think managed funds still remain a worthy consideration for investors with lower amounts to invest. However, you’ll need to do your homework. Is the fund active or passively managed? Maybe compare portfolio allocations from end 2011 to year to date 2013; this should give you some indication. What is the percentage allocation to government bonds? If you’re concerned at the high level perhaps find a managed fund with a lower allocation and switch or split your investment to spread your risk.
ETFs solely invested in government bonds may find it hard to attract new investment once Commonwealth government bonds are listed on the ASX, as they will be more accessible and more easily traded. However those linked to the UBS Bond Composite Index, with some corporate exposure could be an alternative for smaller investors.
Listed hybrids offer better returns but much higher risk. If a managed fund has a 50% allocation to government bonds you just can’t compare it to listed hybrids as the differences in risk are huge. Listed hybrids, because of their high risk nature aren’t a good substitute for bonds that sit higher in the capital structure. They don’t offer the same protection in a declining market as they display more volatility than senior and subordinated bonds and act much more like the underlying equity.
Summary
Investors need an allocation to bonds in their portfolios. Cash doesn’t offer the upside protection via capital appreciation. Direct bond ownership gives investors control and the opportunity to own the best relative value bonds. Managed funds offer the protective benefits of a fixed income allocation, however usually invest similarly to underlying benchmarks and investors pay ongoing fees, but managed funds remain a reasonable option for investors with limited funds.